Unveiling the Shadows: Understanding Vulvar Cancer.
Vulvar cancer is a rare but serious form of cancer that affects the external female genitalia, or the vulva. Despite its relatively low incidence, it can have a significant impact on a woman’s health and well-being. This article aims to shed light on vulvar cancer, exploring its risk factors, symptoms, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and the importance of early detection in managing this condition.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Understanding Vulvar Cancer
Vulvar cancer develops in the external part of the female genitalia, which includes the labia, clitoris, and vaginal opening. Most cases are diagnosed in older women, but it can affect women of any age. The exact cause of vulvar cancer is often unknown, but several risk factors may contribute to its development.
Risk Factors
- Age:
- Vulvar cancer is more commonly diagnosed in older women, with the risk increasing with age.
- HPV Infection:
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is a significant risk factor for vulvar cancer. Certain strains of HPV have been linked to the development of precancerous lesions in the vulva.
- Smoking:
- Tobacco use has been associated with an increased risk of vulvar cancer, particularly in older women.
- Chronic Skin Conditions:
- Chronic skin conditions affecting the vulva, such as lichen sclerosis, can increase the risk of developing vulvar cancer.
Symptoms
Vulvar cancer may present with various symptoms, and it’s essential for women to be aware of any changes in their genital area. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent itching, burning, or tenderness.
- Changes in color or thickness of the skin.
- Pain or discomfort, especially during urination.
- Ulcers, lumps, or sores that don’t heal.
- Bleeding is not related to menstruation.
Diagnosis
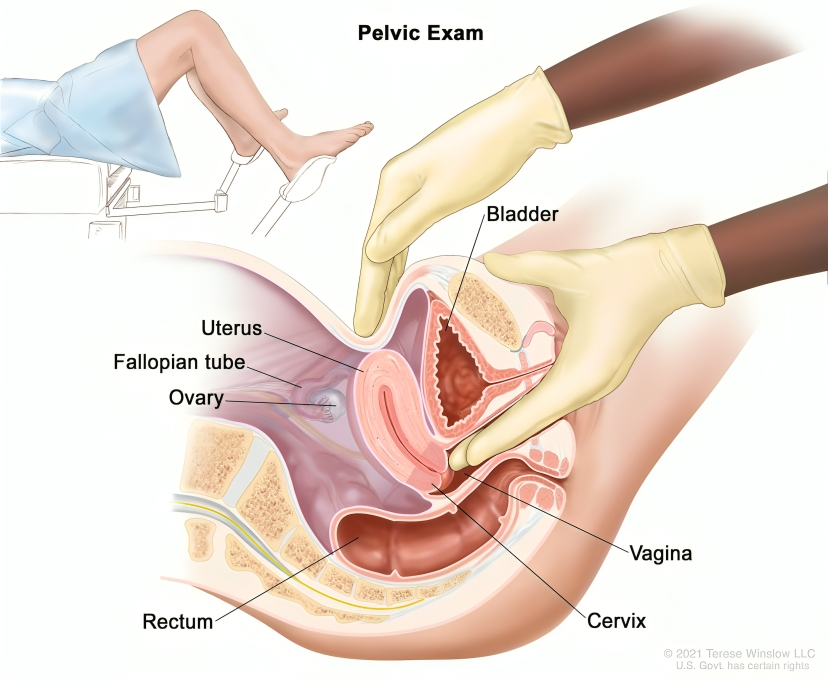
- Physical Examination:
- A thorough physical examination, including a pelvic exam, is often the first step in diagnosing vulvar cancer.
- Biopsy:
- If abnormalities are detected, a biopsy is performed to confirm the presence of cancer and determine its type and stage.
- Imaging Studies:
- Imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scans, may be conducted to evaluate the extent of the cancer and check for potential metastasis.
Treatment Options
Treatment for vulvar cancer depends on the stage of the disease, the size and location of the tumor, and the woman’s overall health. Common treatment options include:
- Surgery:
- Surgical removal of the cancerous tissue is a primary treatment for vulvar cancer. This may involve removing a portion of the vulva or, in more advanced cases, a radical vulvectomy.
- Radiation Therapy:
- Radiation therapy may be used to target and destroy cancer cells, particularly in cases where surgery alone may not be sufficient.
- Chemotherapy:
- Chemotherapy, either alone or in combination with other treatments, may be recommended, especially for advanced stages of vulvar cancer.
Early Detection and Prognosis
Early detection is crucial in improving the prognosis of vulvar cancer. Regular pelvic examinations, particularly for women at higher risk, and awareness of any changes in the vulvar area can contribute to early diagnosis and timely intervention.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Conclusion
Vulvar cancer may be a rare form of cancer, but its impact on affected individuals can be profound. Increased awareness, routine screenings, and understanding of the risk factors associated with this condition are essential in its prevention and early detection. By unraveling the complexities surrounding vulvar cancer, we empower women to take charge of their health and work towards timely interventions that can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life.