The Vital Role of Gynae Oncology: Understanding and Confronting Women’s Cancer.
Gynecologic oncology, often abbreviated as gynae oncology, is a specialized field of medicine focused on the diagnosis, treatment, and management of cancers that affect the female reproductive system. With a deep understanding of the unique anatomy and physiology of the female reproductive organs, gynecologic oncologists play a crucial role in providing comprehensive care to women diagnosed with gynecologic cancers. In this article, we delve into the realm of gynae oncology, exploring the types of cancers it addresses, diagnostic approaches, treatment options, and the importance of multidisciplinary care in improving patient outcomes.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Understanding Gynecologic Cancers
Gynecologic cancers encompass a diverse group of malignancies that originate in the female reproductive organs, including the ovaries, uterus (endometrium), cervix, vagina, vulva, and fallopian tubes. The most common types of gynecologic cancers include ovarian cancer, endometrial cancer, cervical cancer, vaginal cancer, and vulvar cancer. Each type of gynecologic cancer has its unique risk factors, symptoms, and treatment approaches, requiring specialized expertise for accurate diagnosis and optimal management.
Diagnostic Approaches in Gynae Oncology
Early detection and diagnosis are critical in improving outcomes for women with gynecologic cancers. Gynecologic oncologists utilize a variety of diagnostic tools and techniques to evaluate and stage gynecologic cancers, including:
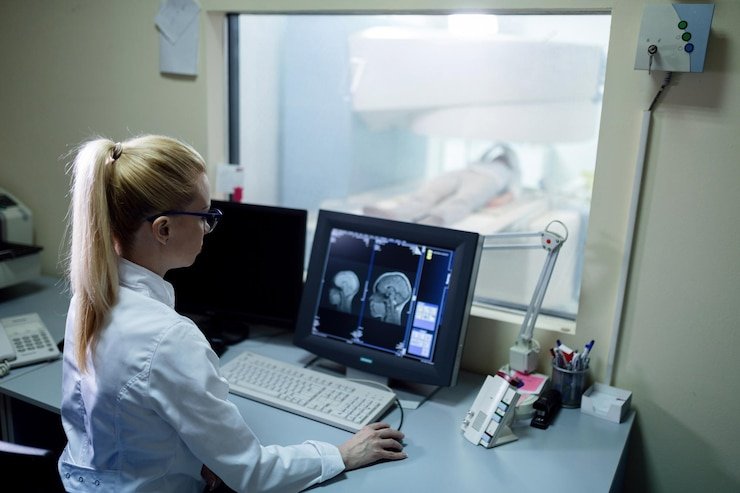
- Imaging Studies: Imaging modalities such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography (PET) scans are used to visualize the extent of cancer and identify metastatic spread.
- Biopsy: Tissue biopsy is often performed to obtain a definitive diagnosis of gynecologic cancers. During a biopsy, a small sample of tissue is collected from the suspected tumor site and examined under a microscope by a pathologist to determine the presence of cancerous cells.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests, including tumor markers such as CA-125 for ovarian cancer and HPV testing for cervical cancer, may be used to assess tumor markers or detect viral infections associated with gynecologic cancers.
Treatment Options in Gynae Oncology
Treatment approaches for gynecologic cancers are tailored to the specific type and stage of the disease, as well as individual patient factors such as age, overall health, and treatment preferences. Treatment modalities may include:
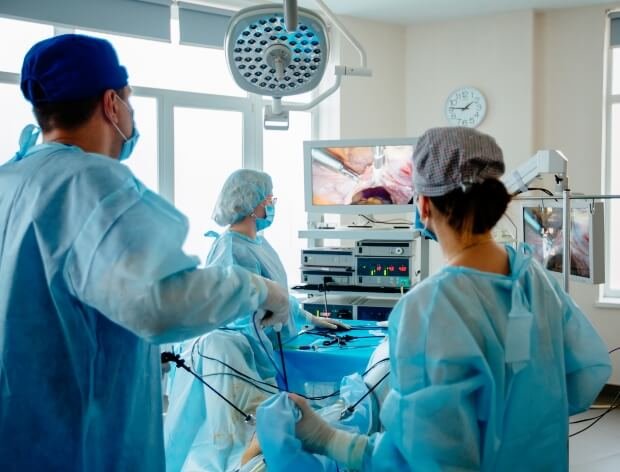
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the cancerous tissue is often the primary treatment for early-stage gynecologic cancers. Gynecologic oncologists are skilled in performing intricate surgical procedures such as hysterectomy (removal of the uterus), oophorectomy (removal of the ovaries), lymph node dissection, and debulking surgery (removal of as much tumor mass as possible).
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves the use of powerful drugs to destroy cancer cells or inhibit their growth. Chemotherapy may be used as adjuvant therapy following surgery to reduce the risk of cancer recurrence or as primary treatment for advanced or metastatic gynecologic cancers.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to target and kill cancer cells. It may be used alone or in combination with surgery and chemotherapy to treat gynecologic cancers, particularly cervical and vaginal cancers.
- Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapy drugs are designed to specifically target cancer cells while sparing normal cells, resulting in fewer side effects. Targeted therapy may be used for certain types of gynecologic cancers that have specific molecular abnormalities, such as HER2-positive endometrial cancer.
Multidisciplinary Care in Gynae Oncology
Gynecologic oncology care often involves a multidisciplinary team approach, with gynecologic oncologists collaborating closely with other healthcare professionals such as medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, pathologists, radiologists, nurses, and support staff. This collaborative approach ensures that patients receive comprehensive, personalized care that addresses their physical, emotional, and psychosocial needs throughout the cancer journey.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Conclusion
Gynecologic cancers pose significant challenges to women’s health, requiring specialized expertise and comprehensive care to achieve optimal outcomes. Gynecologic oncologists play a vital role in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of gynecologic cancers, offering patients hope, support, and personalized treatment plans tailored to their unique needs. Through ongoing research, technological advancements, and multidisciplinary collaboration, gynae oncology continues to evolve, paving the way for improved survival rates and quality of life for women affected by gynecologic cancers.