illuminating Hope: The Role of Radiation Therapy in Cancer Treatment.
In the multifaceted landscape of cancer treatment, radiation therapy stands as a powerful and often indispensable tool. This therapeutic approach employs targeted doses of radiation to eliminate or shrink cancer cells, offering a ray of hope to patients facing various types of cancer. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of radiation therapy, exploring its mechanisms, applications, and the significant impact it has in the ongoing battle against cancer.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Understanding Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy, also known as radiotherapy, involves the use of high doses of radiation to target and damage cancer cells. The primary goal is to disrupt the growth and division of these malignant cells, preventing them from spreading or causing further harm. Radiation therapy may be employed as a standalone treatment or in combination with surgery, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy, depending on the specific characteristics of the cancer.
Types of Radiation Therapy
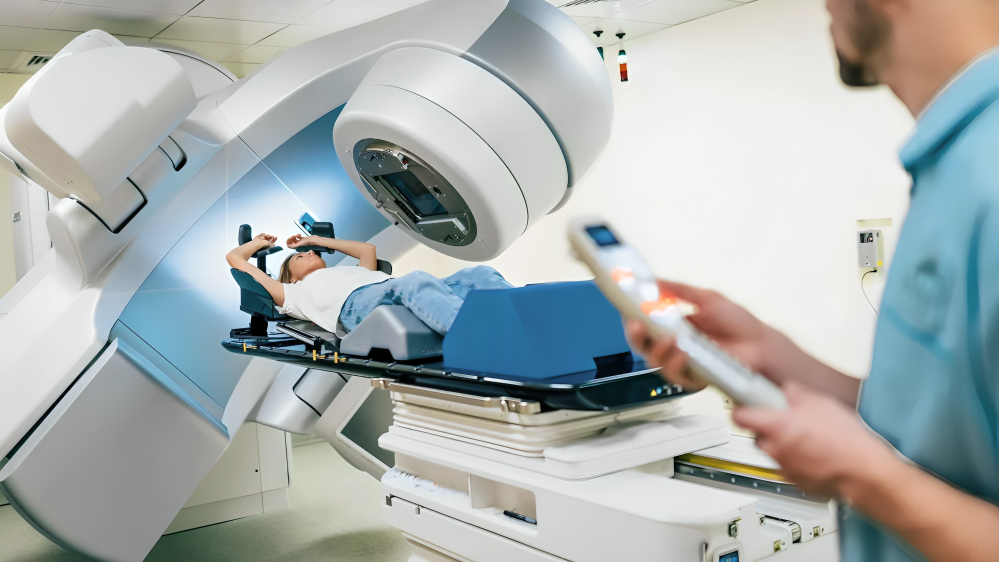
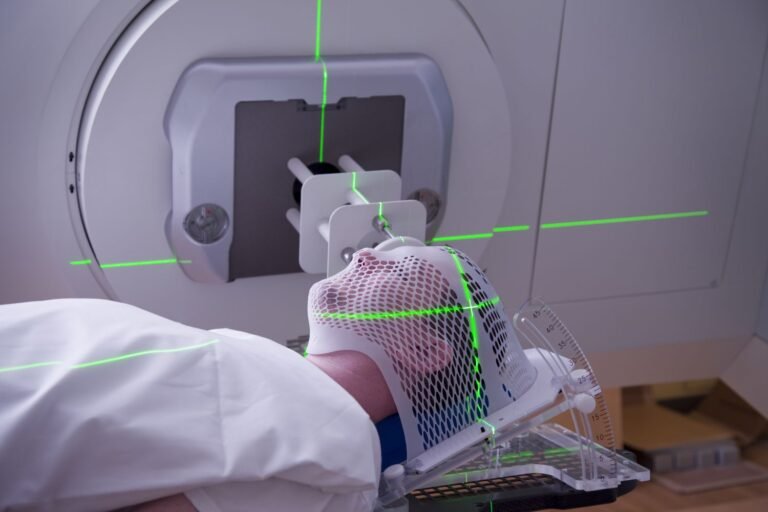
- External Beam Radiation: This is the most common form of radiation therapy, where a machine outside the body delivers precisely targeted beams of radiation to the cancerous area. Advanced techniques such as intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) allow for enhanced precision, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
- Internal Radiation (Brachytherapy): In this approach, radioactive materials are placed directly within or very close to the tumor. Brachytherapy is often used for cancers of the prostate, cervix, and certain other organs, providing a concentrated dose to the affected area.
- Systemic Radiation: This involves the administration of radioactive substances, either orally or intravenously, that travel throughout the body to target cancer cells. Radioactive iodine therapy for thyroid cancer is a notable example of systemic radiation.
Applications of Radiation Therapy
- Curative Intent: Radiation therapy can be employed with the intention of curing cancer, particularly when the disease is localized or in its early stages. The treatment aims to eliminate cancer cells and prevent their regrowth.
- Palliative Care: In cases where a cure may not be possible, radiation therapy can be used to relieve symptoms and improve the quality of life for patients. Palliative radiation is often employed to shrink tumors causing pain or other discomfort.
- Adjuvant Therapy: Radiation therapy may be used after surgery or in conjunction with chemotherapy to eliminate residual cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Neoadjuvant Therapy: Administering radiation therapy before surgery aims to shrink tumors, making them more manageable for surgical removal.
Side Effects and Management
While radiation therapy is a crucial aspect of cancer treatment, it may lead to side effects as it affects both cancerous and healthy cells. Common side effects include fatigue, skin changes, and localized discomfort. Advances in technology and treatment planning have significantly minimized these side effects, and healthcare providers employ various strategies to manage and alleviate any associated discomfort.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Conclusion
Radiation therapy has emerged as a cornerstone in the comprehensive approach to cancer treatment. Its ability to precisely target cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue highlights its efficacy and importance in the fight against cancer. As technology continues to advance, radiation therapy stands at the forefront of innovation, offering hope and healing to individuals navigating the challenging journey of cancer. The ongoing research and development in this field promise even greater precision, effectiveness, and improved outcomes for patients in the years to come.