Understanding Radiation Therapy: A Vital Component in Cancer Treatment.
Radiation therapy, also known as radiotherapy, is a cornerstone in the treatment of cancer. It utilizes high-energy radiation to target and destroy cancer cells while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue. Radiation therapy can be used as a primary treatment to eradicate tumors, as an adjuvant therapy to prevent cancer recurrence, or as a palliative treatment to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. In this article, we’ll explore the principles, techniques, and applications of radiation therapy in cancer treatment.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Principles of Radiation Therapy
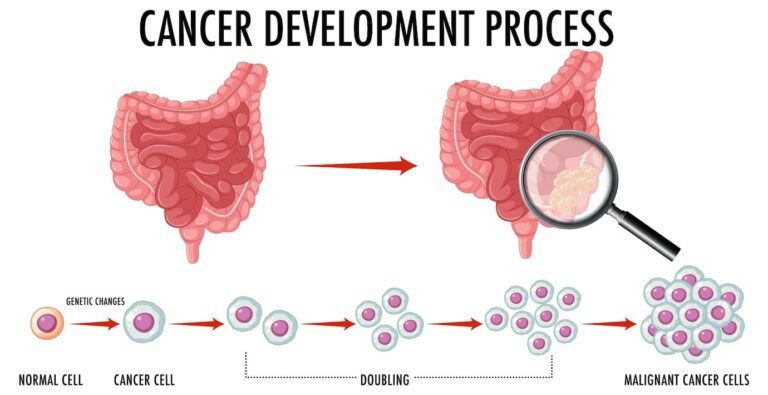
Radiation therapy works by damaging the DNA of cancer cells, disrupting their ability to grow and multiply. Unlike chemotherapy, which circulates throughout the body, radiation therapy precisely targets the tumor site with focused beams of radiation. This localized approach helps minimize side effects and preserve healthy tissue.
Techniques of Radiation Therapy
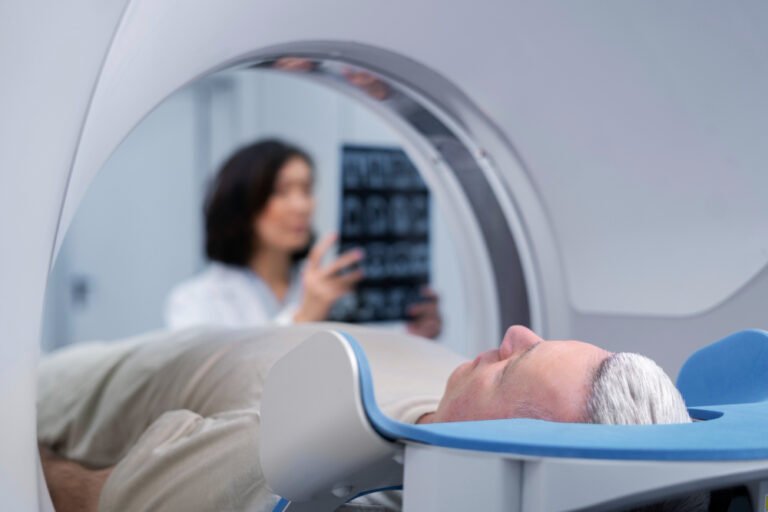
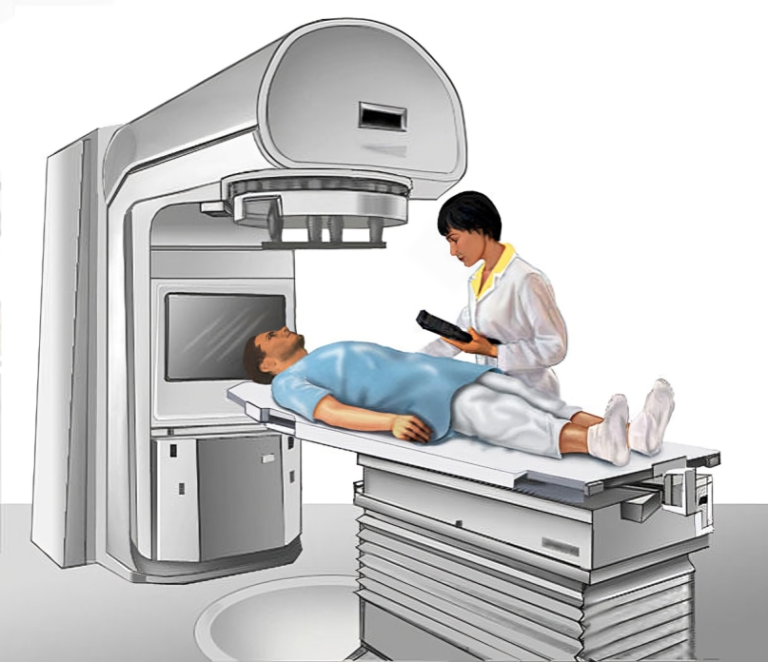
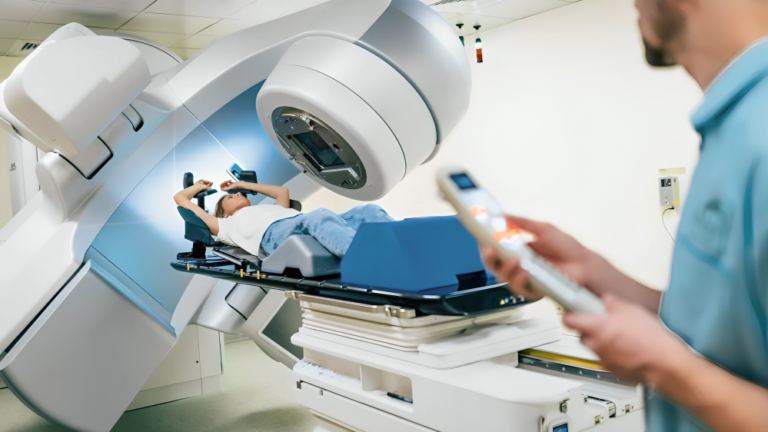
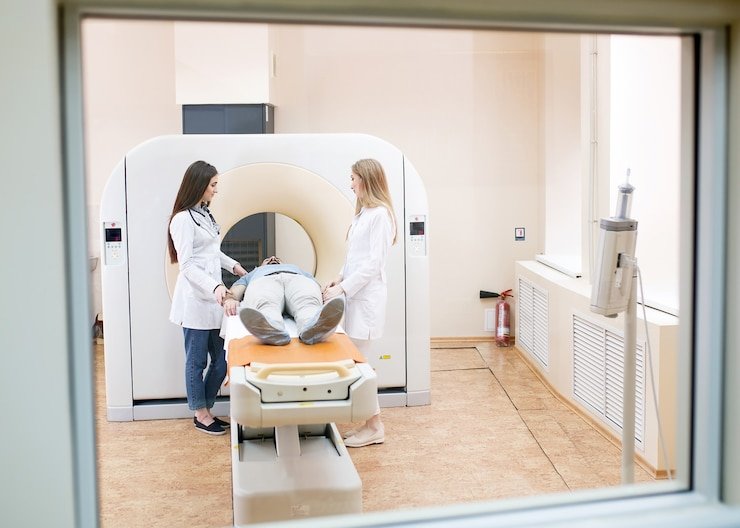
- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT): EBRT is the most common form of radiation therapy, involving the delivery of radiation from an external source. Advanced imaging techniques such as CT scans or MRI are used to precisely map the tumor’s location and shape. High-energy X-rays or protons are then directed at the tumor from different angles to maximize dose delivery while sparing nearby organs and tissues.
- Brachytherapy: Brachytherapy, also known as internal radiation therapy, involves the placement of radioactive sources directly inside or next to the tumor. This allows for the delivery of high doses of radiation to the tumor while minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy tissue. Brachytherapy is commonly used in the treatment of prostate, cervical, and breast cancers.
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT): SRS and SBRT are highly precise techniques that deliver concentrated doses of radiation to small tumors or specific areas within the body. These techniques are commonly used to treat brain tumors, spinal tumors, and early-stage lung cancers. SRS and SBRT are typically completed in fewer treatment sessions than conventional radiation therapy.
Applications of Radiation Therapy
- Curative Treatment: Radiation therapy can be used with the intent to cure cancer by eradicating tumors and preventing their recurrence. It is often combined with surgery and/or chemotherapy to achieve optimal outcomes in certain types of cancer, such as breast cancer, lung cancer, and head and neck cancers.
- Adjuvant Therapy: In cases where cancer has been surgically removed but there is a risk of residual disease, adjuvant radiation therapy may be recommended to eliminate any remaining cancer cells and reduce the likelihood of recurrence. Adjuvant radiation therapy is commonly used in the treatment of breast, prostate, and colorectal cancers.
- Palliative Care: For patients with advanced or metastatic cancer, radiation therapy can provide palliative relief by shrinking tumors, alleviating symptoms such as pain or bleeding, and improving quality of life. Palliative radiation therapy may be used to target specific areas of metastasis or to relieve symptoms caused by primary tumors.
Side Effects and Management:
While radiation therapy is highly effective in treating cancer, it can also cause side effects due to damage to healthy tissue surrounding the tumor. Common side effects may include fatigue, skin irritation, nausea, and hair loss (in areas exposed to radiation). However, advances in radiation therapy techniques and supportive care measures have helped minimize these side effects.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Conclusion:
Radiation therapy plays a vital role in the multidisciplinary approach to cancer treatment, offering curative, adjuvant, and palliative options for patients with various types and stages of cancer. With its precise targeting capabilities and evolving technology, radiation therapy continues to improve outcomes and quality of life for cancer patients worldwide. As research and innovation in radiation oncology continue to advance, the future of cancer treatment holds promise for even greater efficacy and fewer side effects.