Navigating the Landscape of Urological Cancer Understanding Treatment and Hope.
Urological cancers, affecting organs within the urinary system, pose significant challenges to individuals and healthcare professionals alike. This diverse group of cancers includes those affecting the kidneys, bladder, prostate, testicles, and other related structures. In this article, we will explore the complexities of urological cancer, delving into its types, risk factors, diagnostic methods, treatment options, and the evolving landscape of research and hope in the face of these diseases.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Types of Urological Cancers
- Prostate Cancer: Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers in men. It typically develops in the prostate gland and may progress slowly. Early detection through screening, such as the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test, is crucial for effective treatment.
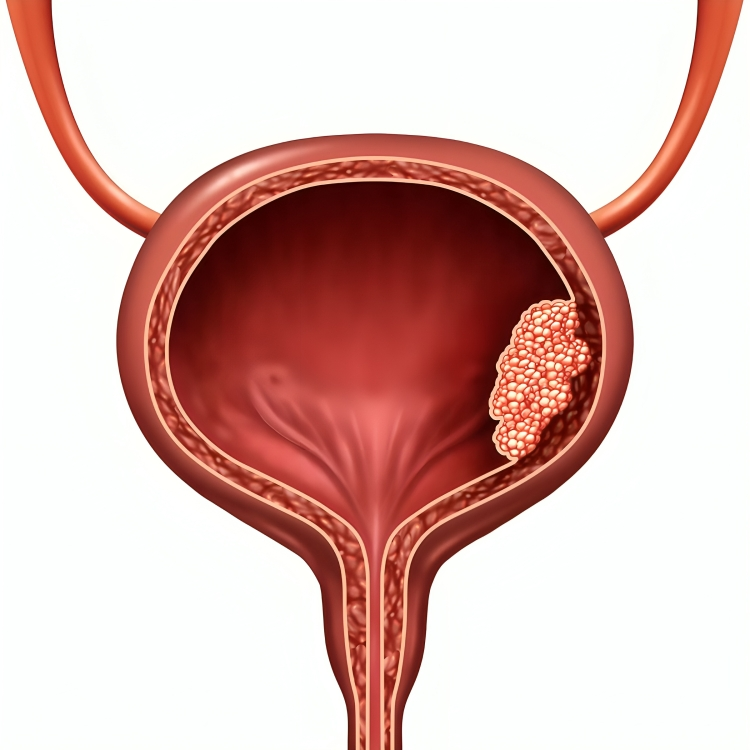
- Bladder Cancer: Bladder cancer can occur in the lining of the bladder and is often characterized by blood in the urine. It is more prevalent in older adults and may be associated with smoking and occupational exposures to certain chemicals.
- Kidney Cancer: Kidney cancer originates in the kidneys and may not exhibit symptoms in its early stages. Imaging tests such as CT scans and ultrasounds play a vital role in diagnosis. Surgery is a common treatment for localized kidney cancer.
- Testicular Cancer: Testicular cancer primarily affects young men and is known for its high cure rate, especially when detected early. Self-examination and regular check-ups contribute to early detection and successful treatment.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Understanding the risk factors associated with urological cancers is crucial for prevention and early intervention. Common risk factors include age, family history, tobacco use, exposure to certain chemicals, and, in the case of prostate cancer, race. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding tobacco, can contribute to reducing the risk of urological cancers.
Diagnostic Methods
Advancements in diagnostic methods have significantly improved the early detection of urological cancers. Imaging techniques, such as CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds, play a pivotal role in identifying tumors and determining their stage. Biopsy procedures provide essential information about the type of cancer and guide treatment decisions.
Treatment Modalities
The treatment of urological cancers depends on various factors, including the type of cancer, its stage, and the overall health of the patient. Common treatment modalities include:
- Surgery: Surgical intervention is often the primary treatment for localized urological cancers, involving the removal of tumors or affected organs.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy utilizes targeted radiation to destroy cancer cells or inhibit their growth. It is frequently employed as part of the treatment plan for bladder and prostate cancers.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill or control the growth of cancer cells. While not always the first line of treatment for urological cancers, it may be employed in cases of advanced or metastatic disease.
- Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapies: These innovative approaches harness the body’s immune system or target specific molecules involved in cancer growth. Immunotherapy has shown promise in the treatment of advanced kidney and bladder cancers.
The Landscape of Research and Hope
Ongoing research continues to uncover new insights into the biology of urological cancers, paving the way for targeted therapies and personalized treatment approaches. Clinical trials offer patients access to experimental treatments and contribute to advancing the field. Additionally, awareness campaigns and educational initiatives aim to encourage early detection and destigmatize discussions around urological health.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Conclusion
Urological cancers present a complex and diverse set of challenges, demanding a comprehensive understanding of risk factors, early detection methods, and evolving treatment options. Advances in medical science and a growing emphasis on holistic patient care are contributing to improved outcomes and a sense of hope for individuals facing urological cancers. By fostering awareness, encouraging preventive measures, and supporting ongoing research, the medical community and society at large can make strides toward a future where the impact of urological cancers is minimized, and individuals receive timely and effective care.