Radiation Therapy: Understanding Treatment, Side Effects, and Patient Care.
Radiation therapy, also known as radiotherapy, is a cornerstone of cancer treatment, playing a crucial role in the management of various malignancies. Utilizing high-energy radiation beams, radiation therapy targets and destroys cancer cells while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues. In this article, we’ll explore the principles of radiation therapy, its applications, common side effects, and the importance of comprehensive patient care throughout the treatment process.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Principles of Radiation Therapy:
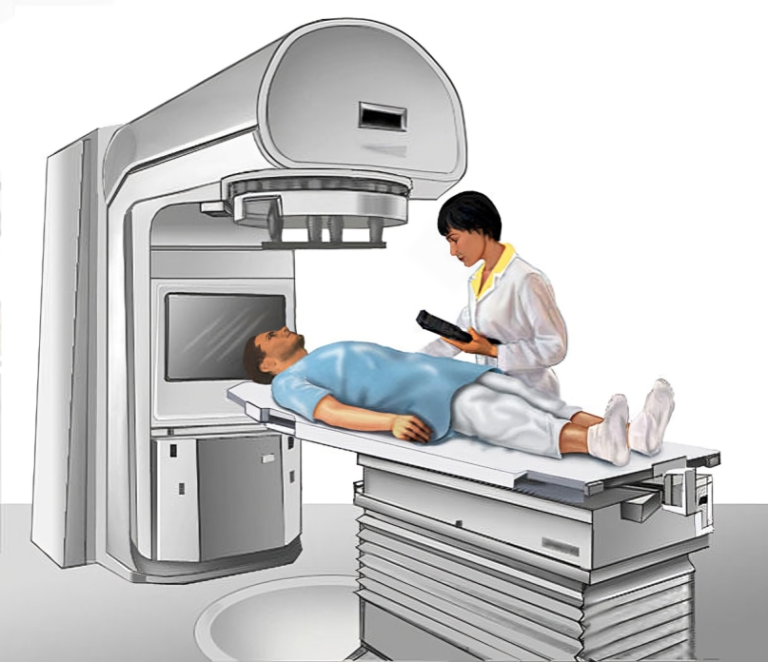
Radiation therapy works by delivering targeted doses of ionizing radiation to cancerous tumors, impairing their ability to grow and divide. This can be achieved through external beam radiation therapy (EBRT), where radiation is delivered from outside the body using specialized machines, or internal radiation therapy (brachytherapy), where radiation sources are placed directly within or near the tumor.
The goal of radiation therapy varies depending on the type and stage of cancer but typically includes:
- Curative Intent: Radiation therapy may be used as a primary treatment modality to eradicate localized tumors, either alone or in combination with surgery, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy.
- Palliative Care: In advanced or metastatic cancers, radiation therapy can alleviate symptoms such as pain, bleeding, or obstruction, improving quality of life and providing comfort to patients.
- Adjuvant Therapy: Radiation therapy may be administered after surgery or other treatments to eliminate any remaining cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Neoadjuvant Therapy: In some cases, radiation therapy may be given before surgery or other treatments to shrink tumors, making them easier to remove or more susceptible to subsequent therapies.
Applications and Techniques:
Radiation therapy can be used to treat a wide range of cancers, including but not limited to:
- Breast cancer
- Prostate cancer
- Lung cancer
- Head and neck cancer
- Brain tumors
- Gynecologic cancers
- Lymphomas
- Skin cancers
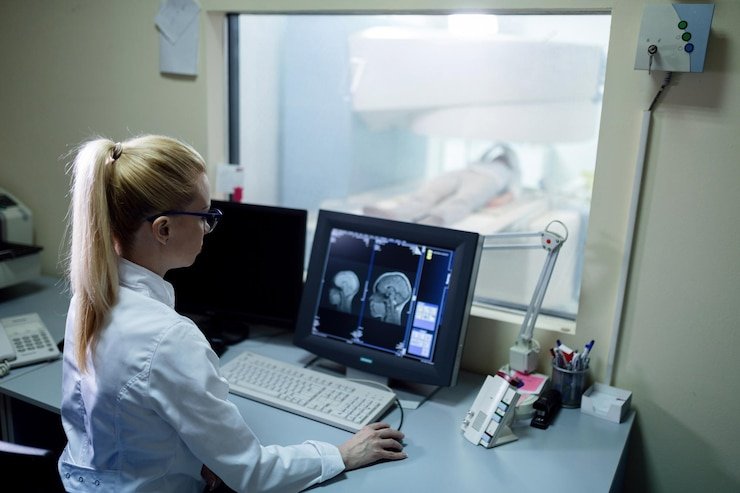
Treatment planning is a collaborative process involving oncologists, radiation therapists, medical physicists, and dosimetrists. Advanced imaging techniques such as CT scans, MRI, and PET scans are utilized to precisely delineate tumor boundaries and optimize radiation delivery while sparing nearby critical structures.
Common Side Effects: While radiation therapy is a highly effective treatment modality, it can also cause side effects due to its effects on healthy tissues adjacent to the tumor. Common side effects may include:
- Fatigue: Many patients experience fatigue, which can range from mild to severe and may persist throughout the course of treatment.
- Skin Changes: Radiation therapy can cause skin reactions such as redness, irritation, dryness, or blistering in the treated area.
- Hair Loss: Hair loss may occur in the radiation field, although this is typically temporary and reversible.
- Nausea and Digestive Symptoms: Radiation therapy to the abdomen or pelvis may cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or changes in appetite.
- Swelling and Lymphedema: Radiation therapy to lymph nodes can lead to swelling and lymphedema in the affected area.
Comprehensive Patient Care:
Comprehensive patient care is essential throughout the radiation therapy process to ensure optimal outcomes and quality of life. This includes:
- Pre-treatment Counseling: Patients should receive thorough education and counseling about the goals, risks, and benefits of radiation therapy, as well as strategies for managing potential side effects.
- Treatment Monitoring: Regular follow-up appointments with the treatment team allow for close monitoring of treatment response, side effects, and overall well-being.
- Supportive Care: Supportive care services such as nutritional counseling, pain management, physical therapy, and psychosocial support can help patients cope with the physical and emotional challenges of cancer treatment.
- Survivorship Planning: As cancer survivorship rates continue to improve, survivorship planning becomes increasingly important, focusing on long-term monitoring, surveillance, and management of late effects and survivorship issues.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Conclusion:
Radiation therapy is a vital component of cancer treatment, offering curative, palliative, and symptom-relieving benefits to patients with various malignancies. By understanding the principles of radiation therapy, its applications, common side effects, and the importance of comprehensive patient care, healthcare providers and patients can work together to optimize treatment outcomes and enhance quality of life throughout the cancer journey. As technology advances and treatment techniques evolve, radiation therapy continues to play an increasingly pivotal role in the fight against cancer.