Navigating the Landscape of Hepatobiliary Cancer: Understanding, Diagnosis, and Treatment.
Hepatobiliary cancer, encompassing cancers of the liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts, presents a complex and challenging landscape in the realm of oncology. This cluster of cancers demands a comprehensive understanding due to its intricate anatomy, diverse risk factors, and varying treatment approaches. In this article, we will delve into the nuances of hepatobiliary cancer, exploring its types, risk factors, diagnostic methods, and contemporary treatment strategies.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Understanding Hepatobiliary Cancer
- Types of Hepatobiliary Cancer:
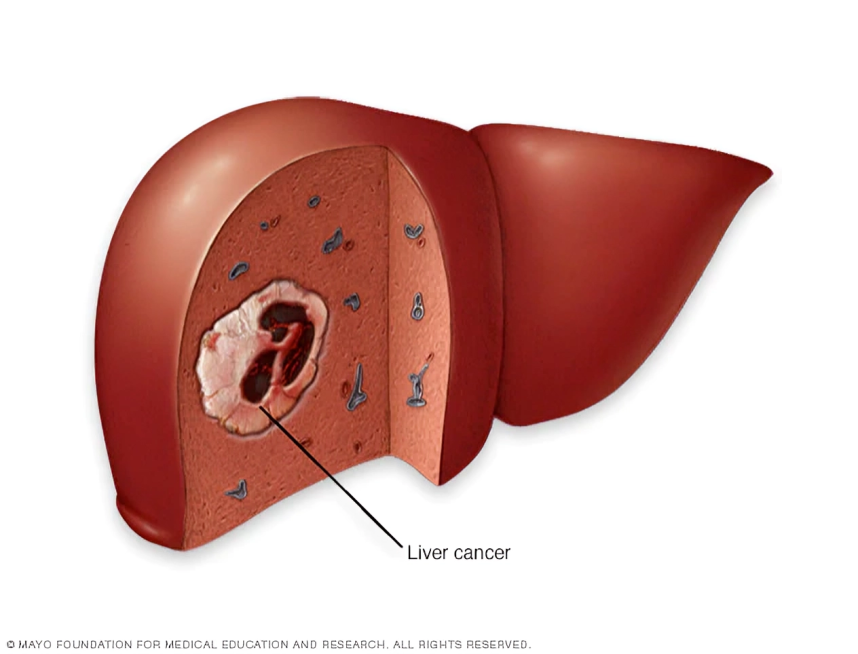
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): The most prevalent form of liver cancer, primarily originating in hepatocytes, the main cells of the liver.
- Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: Arising in the bile ducts within the liver, this cancer accounts for a significant portion of hepatobiliary malignancies.
- Extrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: Occurring in the bile ducts outside the liver, this form poses distinct challenges in terms of diagnosis and treatment.
- Gallbladder Cancer: Though relatively rare, cancer can develop in the gallbladder, often diagnosed at an advanced stage.
Risk Factors
- Chronic Liver Diseases:
- Individuals with chronic conditions such as cirrhosis, hepatitis B or C, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease face an increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Bile Duct Disorders:
- Conditions like primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) and choledochal cysts elevate the risk of developing bile duct cancers.
- Environmental Factors:
- Exposure to certain toxins, aflatoxins, and heavy metals can contribute to the development of hepatobiliary cancers.
- Genetic Predisposition:
- Inherited conditions like Lynch syndrome and hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC) may increase the likelihood of gallbladder cancer.
Diagnosis
- Imaging Studies:
- Computed tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and ultrasound play crucial roles in visualizing tumors and assessing their extent.
- Blood Tests:
- Elevated levels of certain biomarkers, such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and CA 19-9, can provide additional information in the diagnosis and monitoring of hepatobiliary cancers.
- Biopsy:
- Tissue samples obtained through biopsy procedures help confirm the presence of cancer and guide treatment decisions.
Treatment Strategies
- Surgery:
- Surgical interventions, including tumor resection, liver transplantation, and biliary tract surgery, are primary treatment options when feasible.
- Radiation Therapy:
- External beam radiation or brachytherapy may be employed to target and destroy cancer cells in specific locations.
- Chemotherapy:
- Systemic chemotherapy or intra-arterial chemotherapy directly into the liver can be administered to control or eliminate cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapies and Immunotherapy:
- Emerging therapies, such as targeted drugs and immunotherapy, show promise in treating advanced hepatobiliary cancers by targeting specific molecular pathways and enhancing the body’s immune response.
To Know More About It Please Click Here
Conclusion
Hepatobiliary cancer poses unique challenges, demanding a multidisciplinary approach for effective management. As advancements in research and technology continue, the landscape of diagnosis and treatment evolves, offering hope for improved outcomes and a better quality of life for individuals affected by these complex malignancies. Early detection, personalized treatment plans, and ongoing research efforts contribute to the ongoing pursuit of effective strategies in the battle against hepatobiliary cancer.